Background: Idiopathic erythrocytosis (IE) is an entity characterized by a persistently elevated hemoglobin, variable erythropoietin (EPO) level, absence of janus kinase 2 (JAK2) mutations suggestive of polycythemia vera (PV) and no identifiable secondary cause. Previous studies have compared IE to PV, showing a lower incidence of venous thrombosis and leukemic transformation in IE but similar incidence of arterial events. PV is known to be associated with constitutional symptoms and splenomegaly, while hereditary erythrocytosis can be associated with recurrent headaches and fatigue. A comprehensive assessment of clinical features including symptoms in IE has not been performed.
Methods: Patients signed informed consent to participate in an observational study approved by the Institutional Review Board. Enrollment criteria included: age 18 years or older; hemoglobin level greater than 16 g/dL on two occasions at least 3 months apart or greater than 15 g/dL if undergoing phlebotomy; negative testing for JAK2 mutations; and negative work up for secondary causes of erythrocytosis. Baseline assessment included history and physical exam, vital signs, pulse oximetry, and body mass index. Baseline laboratory exams included a complete blood cell count, complete metabolic panel, C-reactive protein, iron panel, ferritin, hemoglobin A1C, erythropoietin level. Abdominal ultrasound was performed to evaluate for splenomegaly. The Myeloproliferative Symptom Assessment Form (MPN-SAF) was used to assess for the presence and severity of a broad range of symptoms that may be expected to occur in patients with IE. The MPN-SAF was administered at baseline and every 6 months thereafter.
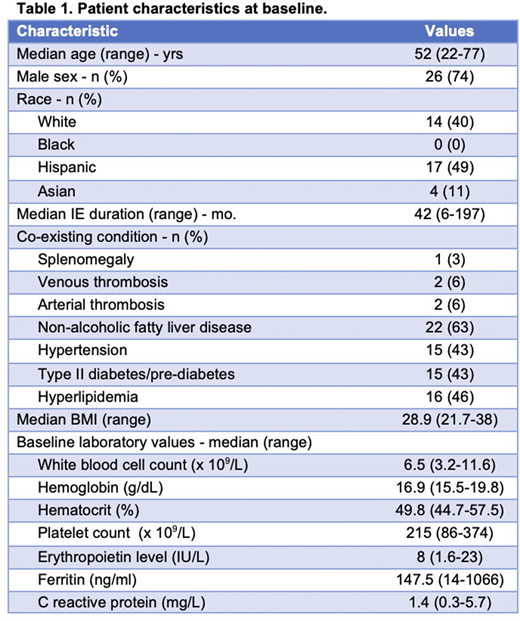
Results: 35 patients had data available for analysis. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. The most prevalent co-morbid conditions were those known to be associated with cardiovascular disease risk and metabolic syndrome, including hepatic steatosis identified on abdominal ultrasound in 63% of patients. Three (8.6%) patients had a history of venous or arterial thrombosis. Two (5.8%) patients had a history of lymphoma (NK/T-cell and Hodgkin). Three patients (8.6%) had a first-degree relative with a myeloproliferative neoplasm (chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, essential thrombocytosis and polycythemia vera) and one patient had a son with IE and history of stroke. 16 (46%) patients were taking aspirin and 11 (31%) had undergone phlebotomy within 3 months of study enrollment. Patients reported the following symptoms on the MPN-SAF at baseline: fatigue (77%), early satiety (57%), difficulty sleeping (57%), numbness/tingling (51%), headaches (49%), concentration problems (40%), itching (40%), bone pain (37%), night sweats (37%), depression (37%), abdominal pain (37%), abdominal discomfort (37%), inactivity (37%), problems with sexual desire/function (34%), dizziness/lightheadedness (31%), cough (26%), fever (17%), and unintentional weight loss (17%). Fatigue carried the highest average symptom intensity (3.77, SD 3.17).
Discussion: In this study, we describe the clinical features associated with IE in a multiracial cohort. Patients with IE are frequently symptomatic and have a high incidence of hepatic steatosis by ultrasound.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal